diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index 9180146..f82ccf3 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -85,7 +85,7 @@ dfs = DeepFace.find(
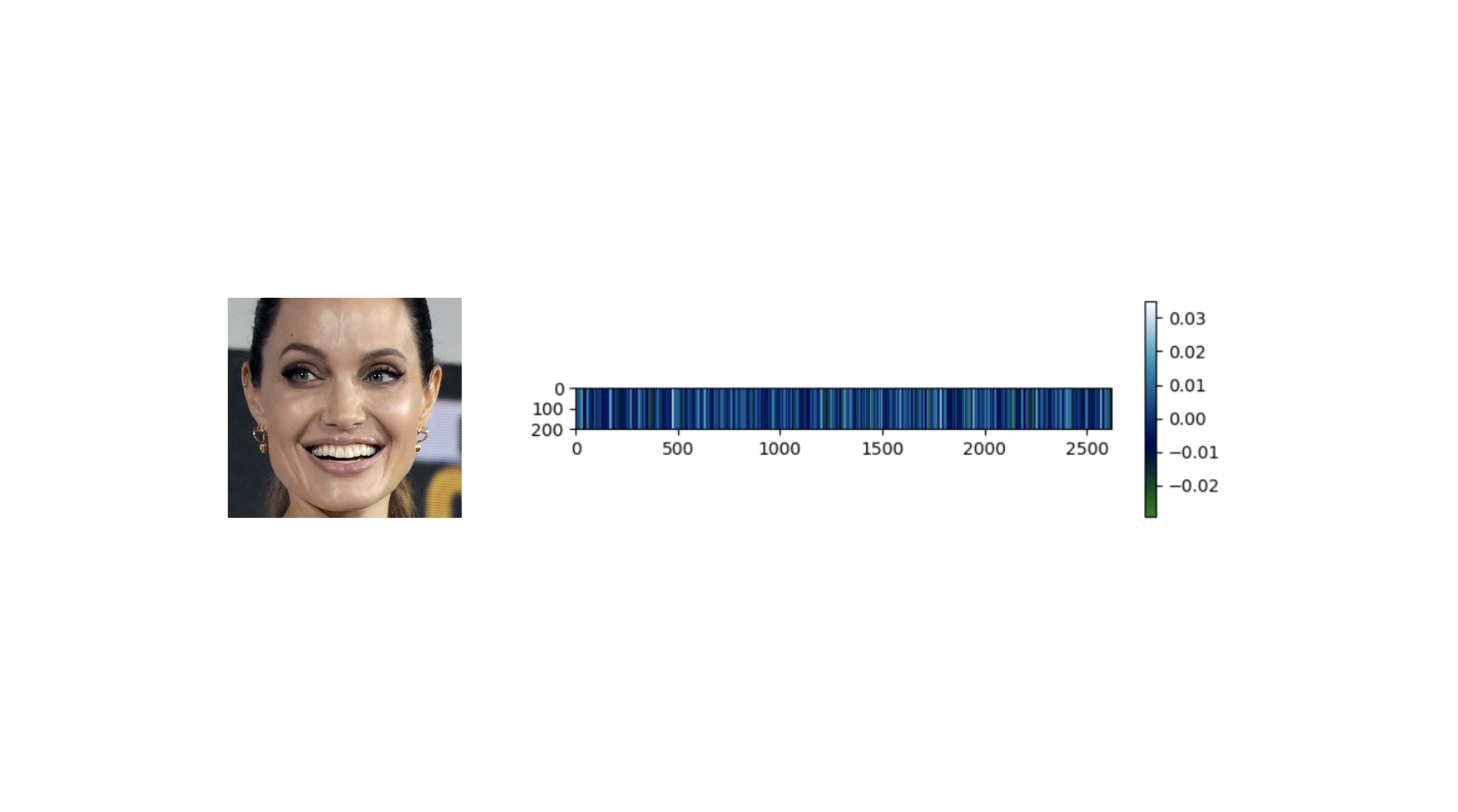
-**Embeddings**
+**Embeddings** - [`Demo`](https://youtu.be/OYialFo7Qo4)
Face recognition models basically represent facial images as multi-dimensional vectors. Sometimes, you need those embedding vectors directly. DeepFace comes with a dedicated representation function. Represent function returns a list of embeddings. Result is going to be the size of faces appearing in the image path.
@@ -111,7 +111,7 @@ Here, embedding is also [plotted](https://sefiks.com/2020/05/01/a-gentle-introdu
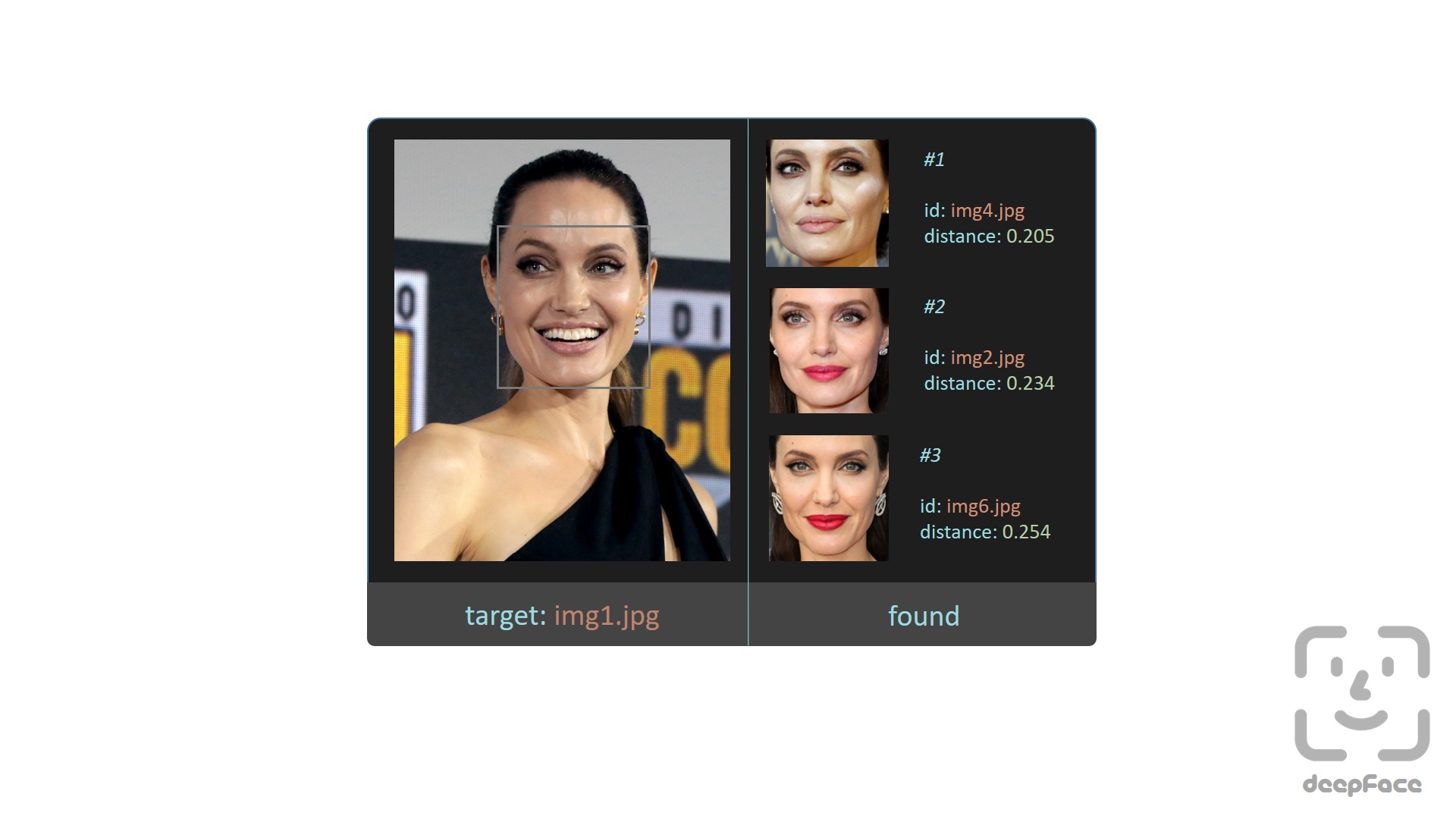
-**Face recognition models** - [`Demo`](https://youtu.be/i_MOwvhbLdI)
+**Face recognition models** - [`Demo`](https://youtu.be/eKOZawGR3y0)
Deepface is a **hybrid** face recognition package. It currently wraps many **state-of-the-art** face recognition models: [`VGG-Face`](https://sefiks.com/2018/08/06/deep-face-recognition-with-keras/) , [`FaceNet`](https://sefiks.com/2018/09/03/face-recognition-with-facenet-in-keras/), [`OpenFace`](https://sefiks.com/2019/07/21/face-recognition-with-openface-in-keras/), [`DeepFace`](https://sefiks.com/2020/02/17/face-recognition-with-facebook-deepface-in-keras/), [`DeepID`](https://sefiks.com/2020/06/16/face-recognition-with-deepid-in-keras/), [`ArcFace`](https://sefiks.com/2020/12/14/deep-face-recognition-with-arcface-in-keras-and-python/), [`Dlib`](https://sefiks.com/2020/07/11/face-recognition-with-dlib-in-python/), `SFace` and `GhostFaceNet`. The default configuration uses VGG-Face model.
![]()
![]()